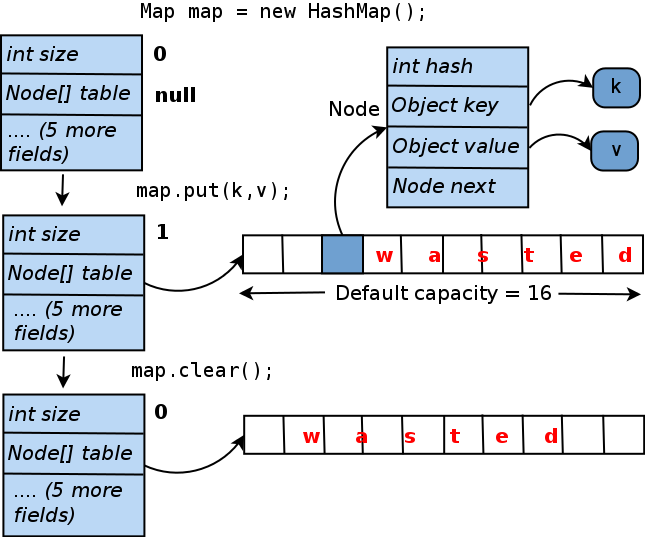
How Map Hashset Works Internally. How the value is fetched by key. On the other hand, a HashSet is an implementation of Set. We will understand this with an example. A Map maps keys to values. I know HashSet internally work as HashMap and HashMap internally use LinkedList as FIFO etc. Implementation details illustrate how the HashSet works internally and leverages the HashMap's put method: public boolean add(E e) return map.put (e, PRESENT) == null ; Copy In this article, we will see how the hashmap get and put method works internally. Let us see the output of the following program which try to add duplicate elements in a HashSet. import java.util. A Set is designed to match the mathematical model of a set.
![How HashSet works in Java [Explained with Example] | Java67](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-IKfgEwKFcOI/YMl703h-VaI/AAAAAAAAoPk/WDol6quYFbwaQtew51b-0kBnoaxKN4F4wCLcBGAsYHQ/w1200-h630-p-k-no-nu/image.png)
How Map Hashset Works Internally. How the value is fetched by key. When we create a HashSet, internally a HashMap is created. It represents the type of element storing in the HashSet. So my Question is when I insert values in StudentRecord class object in pattern like. I know HashSet internally work as HashMap and HashMap internally use LinkedList as FIFO etc. How Map Hashset Works Internally.
Programming languages such as Java provides a feature called 'collections' to store data dynamically.
However, not many programmers know that HashSet uses HashMap internally in java.
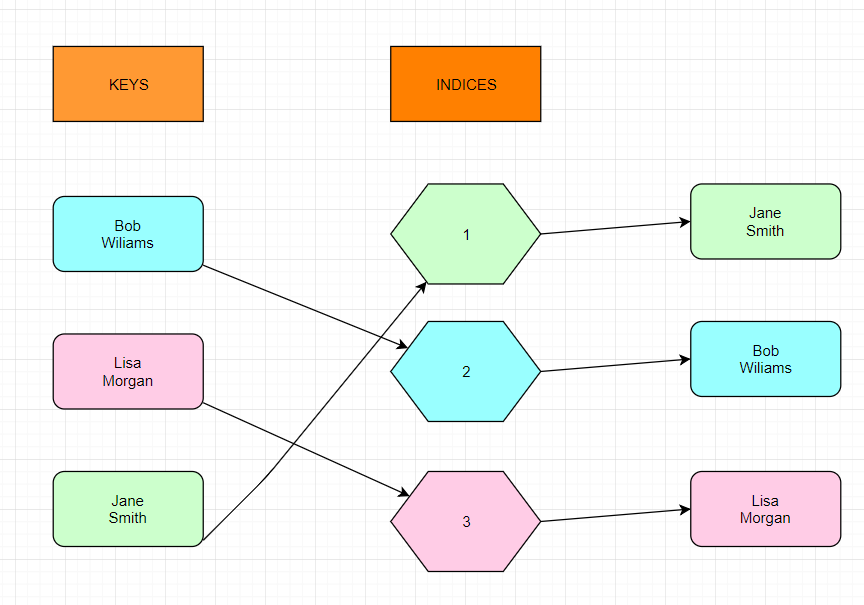
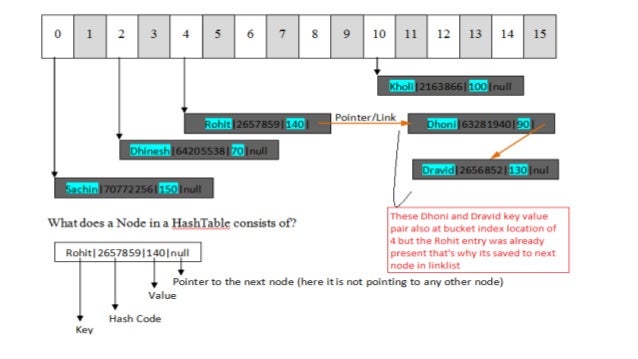
How Map Hashset Works Internally. Hashmap internally do not implements hashset or any set for its implementation. No guarantee is made as to the iteration order of the hash sets which means that the class does not guarantee the constant order of elements over time. However, it implements an entirely different interface. Internally it will call the keyset of the HashMap, as values are stored as keys in the HashMap so what we'll get is the values stored in the HashSet. How the key-value pair is stored.
How Map Hashset Works Internally.